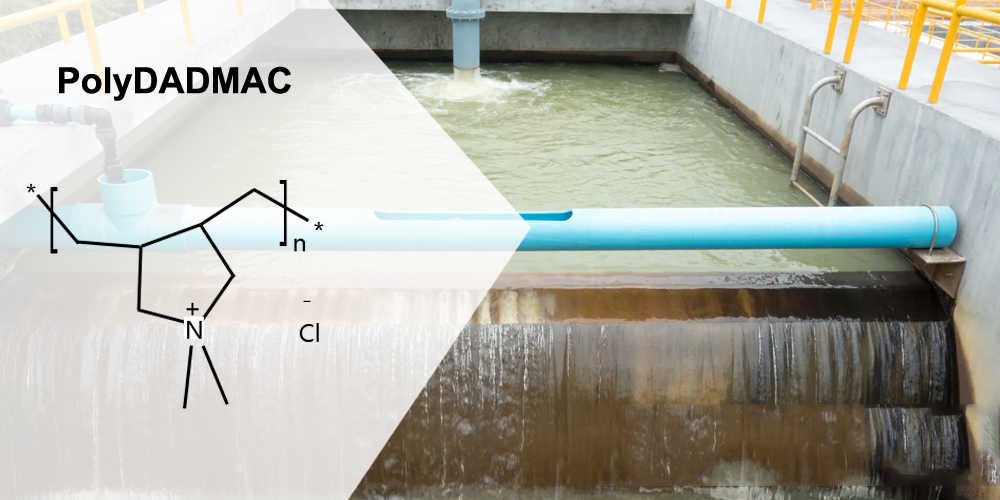
ПолиДАДМАК, чији је пуни назив полидиметилдијалиламонијум хлорид, је катјонски полимер растворљив у води који се широко користи у области пречишћавања воде. Због своје јединствене густине катјонског наелектрисања и високе растворљивости у води, ПолиДАДМАК је ефикасан коагулант који може ефикасно уклонити замућеност, боју и друге нечистоће у води. Међутим, у практичним применама се често користи као...флокуланту комбинацији са другим коагулансима за третман индустријских отпадних вода.
Карактеристике и механизам деловања PolyDADMAC-а
ПолиДАДМАК брзо адсорбује и агрегира негативно наелектрисане колоидне честице и суспендоване чврсте материје у води због своје високе густине катјонског наелектрисања. Његов механизам деловања се углавном заснива на електростатичком привлачењу, што узрокује да се ове ситне честице агломерирају у велике честице, тако да се могу ефикасно уклонити током накнадних процеса таложења или филтрације.
Механизам флокулације PolyDADMAC-а
Флокулација је један од корака у процесу коагулације. Односи се на процес у којем се
„Мали цветови стипсе“ формирани током процеса коагулације формирају флокуле са већим честицама путем адсорпције, електричне неутрализације, премошћавања и хватања мрежом.
У индустрији пречишћавања воде, адсорпција и електрична неутрализација се класификују као коагулација, док се премошћавање и нето-хватање класификују као флокулација. Одговарајуће хемикалије се називају коагуланти и флокуланти, респективно.
Генерално се верује да ПолиДАДМАК има три механизма деловања: адсорпцију, електричну неутрализацију и премошћавање. Прва два су главна. Зато се ПолиДАДМАК класификује као коагулант. Међутим, већина људи коагулацију и флокулацију сматра истим процесом, па се ПолиДАДМАК назива и флокулантом.
У процесима пречишћавања воде, PolyDADMAC се углавном користи као флокулант за побољшање квалитета воде. Конкретно, катјонска кватернарна амонијумова со група PolyDADMAC-а може генерисати електростатичко привлачење са анјонским суспендованим честицама или колоидним честицама у води, што резултира неутрализацијом, формирањем флокула већих честица и њиховим таложењем. Ове флокуле се одвајају током накнадног процеса седиментације или филтрације како би се пречистио квалитет воде.
Предности PolyDADMAC-а
У поређењу са традиционалним флокулантима (стипс, PAC, итд.), PolyDADMAC има следеће значајне предности:
Ефикасно: PolyDADMAC може брзо уклонити нечистоће у води и побољшати квалитет воде.
Једноставан за употребу: Његова употреба је једноставна, само га додајте под одговарајућим условима.
Одрживост: ПолиДАДМАК има добру стабилност и не разграђује се лако као полиакриламид.
Јак ефекат флокулације: Катјонска кватернарна амонијумова со даје PDMDAAC-у јаку способност флокулације, чиме се ефикасно третирају различите квалитете воде;
Добра отпорност на соли, киселине и алкалије: PDMDAAC је погодан за сложене услове квалитета воде и даље има стабилне перформансе флокулације под високим салинитетом, киселим или алкалним условима;
Ниска цена: PolyDADMAC има високу ефикасност флокулације и ниску дозу, што може смањити трошкове пречишћавања воде.
Низак садржај муља: PolyDADMAC производи мање муља од неорганских коагуланата и флокуланта и штеди трошкове постпродукције.
Дозирање и мере предострожности при коришћењу полиДАДМАК-а
Приликом коришћења PolyDADMAC-а, треба строго поштовати оперативне процедуре како би се осигурали оптимални резултати третмана и избегли могући нежељени ефекти. Обично се након додавања флокуланта као што је полиалуминијум хлорид, додаје PolyDADMAC како би се постигао најбољи ефекат коагулације. Поред тога, дозу треба прилагодити квалитету воде и захтевима третмана. Одговарајућа доза може се одредити тестовима у тегли.
Све у свему,ПолиДАДМАКигра важну улогу у области пречишћавања воде. Дубље разумевање његових својстава и примене помоћи ће да се овај производ ефикасније користи за побољшање квалитета воде и заштиту животне средине.
Време објаве: 14. новембар 2024.

